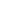Production technology provides the highest rate in the industry >17 pipes per hour
Loading
Sheets for the production of pipes are delivered to the plant by rail or road. transport and unloaded into the sheet storage area. From the storage area sheets, using a lifting beam with vacuum or magnetic gripper are fed into the sheet loading and edge preparation area. In the sheet loading area, sheets are loaded onto conveyor and are sent to the area of the milling machine. We strictly control the quality of the sheet. Works at supplying companies independent inspection.
Shot blasting
Before milling, the sheet passes through a shot blasting section, designed to remove rust, scale, dirt and dust from the sheet before sheet getting into the working area.
Edge processing
Both longitudinal edges are processed on a milling machine. The necessary the shape of the chamfer for welding and the specified width of the sheet.
Roll forming
Forming takes place with the help of a three-roll plate bending machine with pre-stressed top roll in 3-4 passes. This is the only one in the world machine capable of both roll forming and step-by-step operation moldings. Hydraulically controlled bending unit allows perform bending in a wide range of standard sizes on a par with non-standard. Quick changeover to different sizes is an advantage in terms of compared to any compression molding process.
Edge bending
Straight sections at the ends of the sheet are bent to the required diameter on the installation edge folds. The final formed billet with a gap is sent to joint welding.
Assembly and welding of the technological seam
The joint welding unit is designed for continuous welding of the root weld with outside of the pipe. This section uses continuous single arc welding. in a protective gas environment. An integral part of this process are hydraulic clamps that serve to close the gap and align the edges in height.
Visual inspection of the technological seam
In the zone of visual control of the connecting seam, in addition to the inspection itself, automatic recording of welding process parameters and control of edge displacement
Welding of lead strips
Lead-outs are manually welded before final internal and external welding. strips at both ends of the pipe. Process before and after pipe welding. In the same area can be produced inspection and, if necessary, repair of the technological seam.
Internal welding
Internal welding is carried out using a four-arc welding system under the layer flux. Welding is carried out continuously from one lead strip to another and penetrates in the connecting seam.
Pipe cleaning
At the site of internal cleaning of the pipe using metal brushes and a system vacuum suction removes scale and dirt after welding the inner seam.
Outdoor welding
External welding is the final welding process and is carried out using five-arc submerged arc welding system, for complete absorption connecting seam and penetration into the internal welding seam. As a result a unique connection is formed with a strength no less than that of the rest of the material pipes.
Visual inspection of the weld
In the electric pipe welding shop, the pipe undergoes preliminary control: after welding the pipe is inspected by QCD specialists in order to prevent defects, which subsequently cannot be eliminated.
Ultrasonic control I
Before the expansion operation, ultrasonic testing of all pipes is carried out on the presence of defects of any orientation along the entire length of the weld.
X-ray television control I
Pipes with defects are sent to the continuous x-ray television control for the study of defects. Detected defects are eliminated manually, after which the pipe is returned to x-ray station to check the results of the seam repair.
Expansion
Using a mechanical expander, the pipe diameter is calibrated and straightened pipes in the longitudinal direction. In addition to calibration, expansion increases the limit fluidity of the material by 5 - 8%. Removal of expander oil residues from the inner surface of the pipe is carried out at the washing station immediately after expansion using high pressure water pressure.
End chamfering
Pipe end processing equipment is designed to bevel at the same time at both ends of the pipe, which guarantees high quality in terms of perpendicularity and chamfer shape.
Hydraulic test
The equipment is designed to fill the pipe with water and pump the necessary pressure standards. The pipe along its entire length must not leak under pressure in standards.
Ultrasonic control II
After hydrotesting, a second ultrasonic testing station is located for detection of defects in the weld along with the inspection of pipe ends along the entire circumference in all pipes.
X-ray television control
Installation of X-ray television control allows you to additionally confirm weld quality over the entire length of the weld and at a distance of 20 cm from each end pipes.
Magnetic particle testing
To ensure compliance with special standards, after the RTK II section, a additional piece of equipment for non-destructive testing - installation magnetic particle control.
Final Geometry Check
After all tests, the weight and length of the pipe are automatically determined. These the data is transferred to the marking device.
Ultimate Control
The most important area of control, it is from here that the products are sent to the consumer QCD specialists decide whether the pipe meets all the requirements.
Motor transport
Delivery of products to various regions of the country is also possible by road.
Rail
The indisputable advantage of the enterprise is a convenient geographical location. Transport logistics is provided by a large railway junction, connecting the capital with the northern regions. Through a well-established system transportation and full loading of the train, the delivery time is reduced by approximately third.